
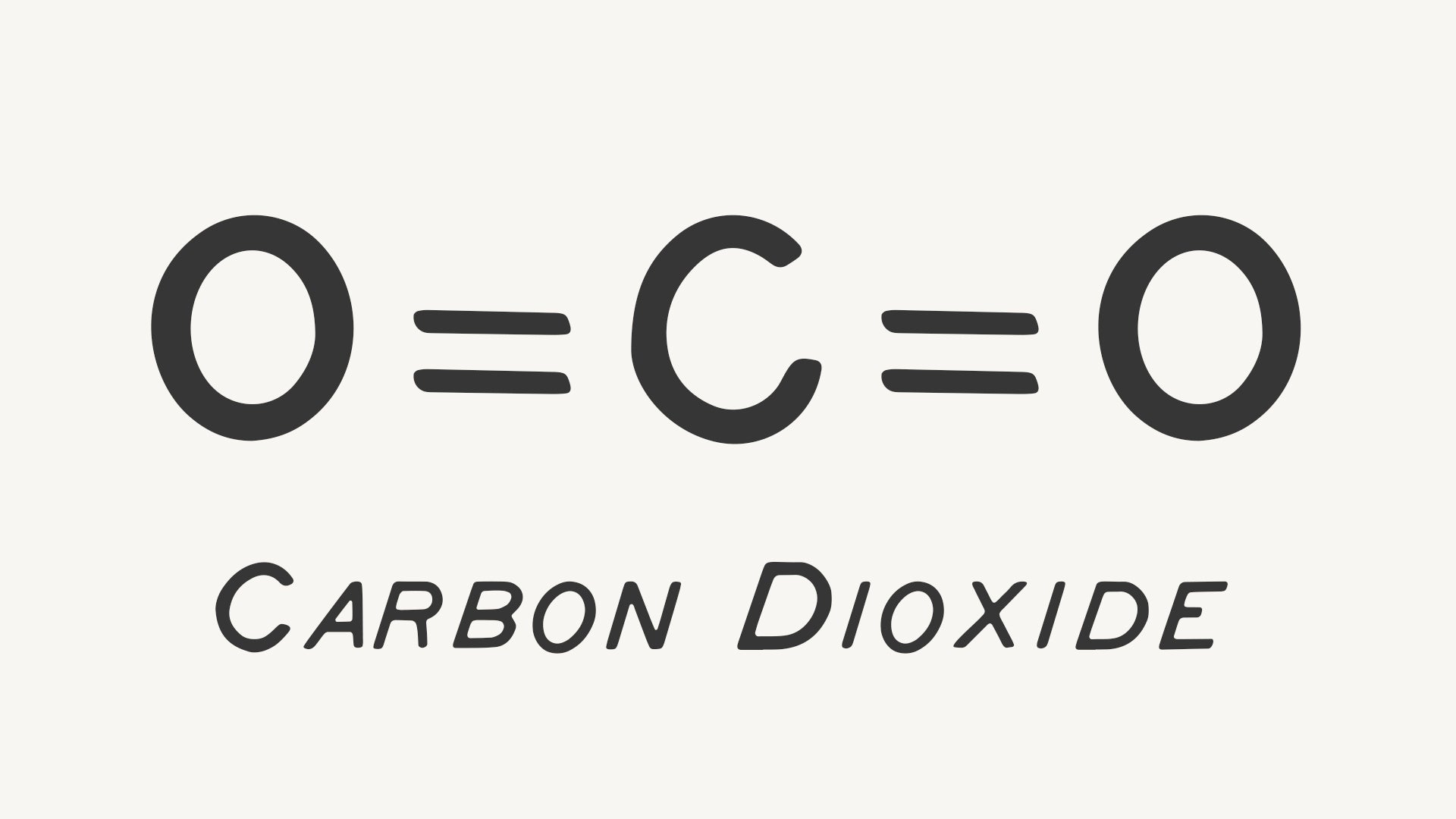
The sensor sends its data to a monitor, where it is displayed in two ways. This allows the sensor to determine how much carbon dioxide a patient exhales. Carbon dioxide absorbs infrared light, so the more CO2 is present, the less light is picked up by the sensor. How CO2 Monitors WorkĬO2 monitors work by shining infrared light across the patient’s breathing tube. This means it doesn’t have to be invasive. However, it can also be done using nasal cannula. A healthy CO2 level means that the patient is breathing well overall.Ĭarbon dioxide monitoring is usually done with an endotracheal tube. They must have good circulation to return waste CO2 to the lungs from body tissues, and have good cellular respiration within the tissue. They have to be taking air into the lungs, and have good alveolar respiration within the lung space. In order to produce a healthy level of CO2, the patient’s breathing has to be healthy. This gives health care providers an overall assessment of the patient’s ventilation. What is CO2 Monitoring?ĬO2 monitoring, or capnography, monitors the amount of carbon dioxide a patient exhales. Keep reading to learn what carbon dioxide monitoring is, why you should use it, and what your top industry equipment options are. That’s why we’ve put together your complete guide on CO2 monitoring and how it can improve your patient outcomes. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier 2020:chap 110.In 2011, a study found that 82% of critical care incidents that led to brain injury and death could have been prevented using one method of carbon dioxide monitoring.Ĭarbon dioxide monitoring a noninvasive, inexpensive, and often underused way to monitor patient status. In: Ronco C, Bellomo R, Kellum JA, Ricci Z, eds. Acid-base physiology and diagnosis of disorders. Syndrome of inappropriate diuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)ĭelirium may also alter bicarbonate levels.Salicylate toxicity (such as aspirin overdose).Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (used to treat glaucoma).What Abnormal Results MeanĪbnormal levels may be due to the following problems: Some laboratories use different measurements or may test different specimens. The example above shows the common measurement range of results for these tests. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results. Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. The normal range is 23 to 29 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L) or 23 to 29 millimoles per liter (mmol/L). The kidneys help maintain the normal bicarbonate levels.

This may cause an imbalance in your body's electrolytes.ĬO2 levels in the blood are affected by kidney and lung function. Changes in your CO2 level may suggest that you are losing or retaining fluid. The CO2 test is most often done as part of an electrolyte or basic metabolic panel.

You may also feel some throbbing at the site after the blood is drawn. You may feel slight pain or a sting when the needle is inserted.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
